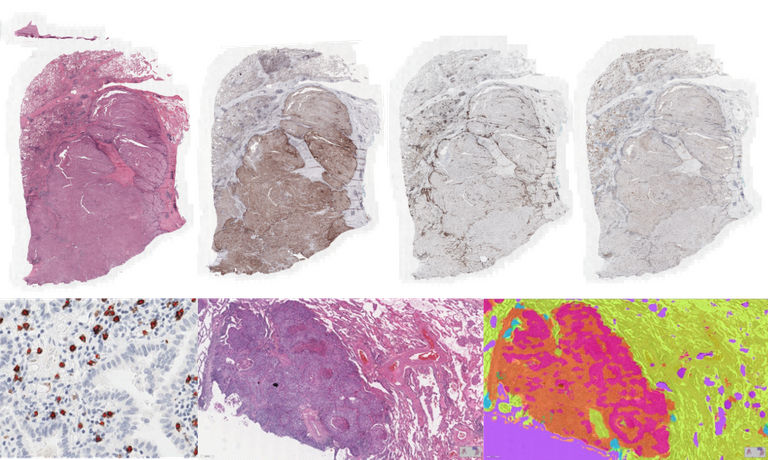
Background
Immunotherapy is a Nobel Prize winning approach to treat cancer patients, which has given spectacular responses in some previously untreatable cancer patients. However, many patients do not respond to immunotherapy and are only exposed to the toxicity of the drugs. Additionally, the cost of immunotherapy treatment is very high (~100kEuro per patient), which puts a dramatic financial burden on the healthcare system. In this context, there is an urgent need for identifying responders and non-reponders at an early stage, to guarantee an efficient and personalized cancer treatment with immunotherapy. In this project, Artificial Intelligence models will be used to challenge one of deadliest of the diseases: lung cancer. AI has the potential to extract and discover features in histopathology images that correlate with treatment response. Therefore, AI models will be developed to predict immunotherapy treatment response of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) patients.
Research question: Is it possible to predict immunotherapy treatment response in NSCLC patients via histopathology image analysis?
Tasks
AI will be leveraged to build machines for automatic assessment of biomarkers based on the analysis of digitalized histopathology images. Computational Pathology models will be developed for the characterization of the immune reaction of the organism in the presence of lung cancer, by extracting biomarkers based on assessment of cytotoxic T-cells (CD8), immune checkpoints (PD-L1), Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs), tertiary lymphoid structures (TLS), among others, guided by the characterization of tissue morphology and composition of histopathology whole-slide images using deep learning methods. The goal is to develop a framework based on the synergy of digital pathology and AI for accurate classification of the tumor immune microenvironment of NSCLC to allow personalization of immunotherapy. Multiple student projects are available in the context of this research. Examples of available projects and tasks are the following:
- Detection of PD-L1 positive cells with deep learning models for object detection and segmentation
- Detection of lung cancer tumor cells in H&E images with deep learning
- Detection of lymphocytes in H&E images of lung cancer
- Detection of macrophages in CD68 stained whole-slide images of lung cancer
- Segmentation of several compartments of lung tissue with deep learning segmentation models
- Classification of lung cancer subtypes using weakly supervised learning
For each task, the student is expected to develop a demonstrator that allows to run the built AI model/pipeline on new whole-slide images.
Contact the supervisor of this project for more information about availability of projects.
Requirements
- Students with a major in artificial intelligence, computer science, biomedical engineering, physics, or a related area in the final stage of master level studies are invited to apply.
- Interest in medical image analysis
- Affinity with programming in Python and with deep learning packages (e.g., TensorFlow, PyThorch) is required.
Information
- Project duration: 3-9 months
- Location: the Diagnostic Image Analysis Group at Radboud University Medical Center
- For more information please contact Francesco Ciompi
